One in all my ongoing tasks is to study extra about how analysis in studying is utilized inside particular fields. You possibly can learn my overview of books summarizing the literature on language studying right here and studying physics right here.
To that finish, I learn Motor Studying and Efficiency, written by the eminent researchers Richard Schmidt and Craig Wrisberg.
This textbook is wide-ranging and filled with fascinating tidbits that don’t match neatly into the overarching principle the authors suggest. (For example, do you know that motion accuracy tends to worsen as we transfer quicker—besides this pattern reverses when muscle tissue are above 70% of their peak pressure. Thus, if you wish to strike a ball extra precisely, surprisingly, you’ll do higher should you swing your hardest!)
However as a substitute of digging into exceptions, at this time, I’d wish to overview the central paradigm of motor expertise argued for by the authors and recommend some implications for enhancing how we study to maneuver.
However First, What Precisely is a Motor Ability?
Everyone knows that studying to do algebra is totally different from studying to play tennis. However what, precisely, is the distinction?
In a way, all expertise we study are motion expertise. Even writing, hardly the standard area of high-school jocks, is simply potential by means of coordinated motion of your fingers to supply the pencil marks or keystrokes wanted.
Equally, few athletic expertise are completely devoid of mental content material. Deciding how you can return a tough tennis serve or determining the most effective path to ski down a mountain all require quick, subtle judgements. Finesse, not simply health, is central to athleticism.
Performing any talent, whether or not it’s athletic or mental, breaks down into roughly three elements:
- Notion. Data from the surface world and sensations from inside your physique should be processed to interpret and perceive the state of affairs you face.
- Determination. Reminiscence and knowledge processing should mix to determine what you must do.
- Motion. The talent should be executed by means of transferring the physique, which could be so simple as uttering a command to a subordinate or writing the reply to a calculation, or as difficult as as taking part in a solo concerto.
The area of express motor expertise, then, includes conditions the place the third factor is a considerable level of problem, as a result of the motion requires excessive levels of pace, accuracy or bodily energy.
My total impression from Schmidt and Wrisberg is that there’s an important continuity between studying motion expertise and studying other forms of expertise. Subsequently, as a substitute of reviewing all the weather of their principle that overlap with what I’ve mentioned elsewhere, I’ll give attention to the facets extra specific to motor expertise.
The Conceptual Mannequin of Motor Expertise
Schmidt and Wrisberg’s textbook regularly builds on a central diagram that illustrates the general principle of how we carry out motor expertise:
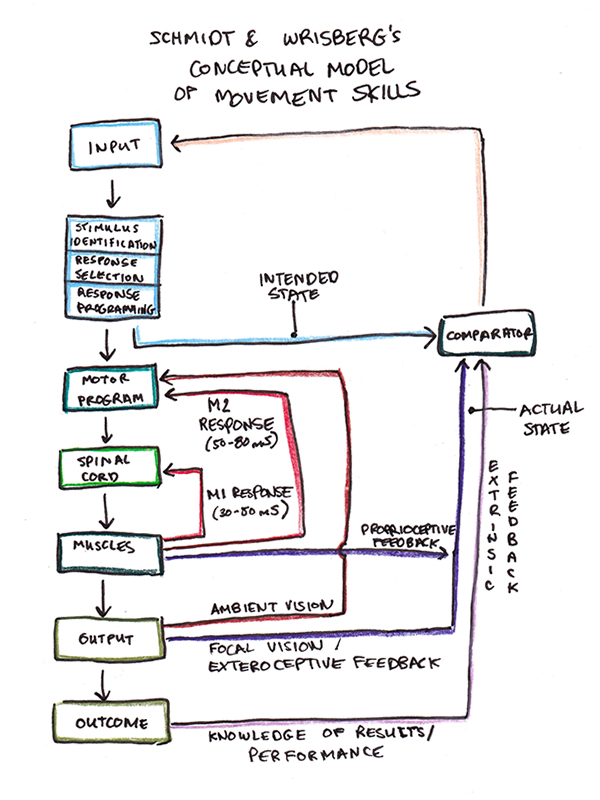
There’s rather a lot to unpack on this picture, however the fundamental thought is that motion includes three phases: notion, resolution and motion, that are embedded in varied suggestions loops together with your physique and the setting.
A key factor on this diagram is the significance of timing. Alerts about what you understand and how you can transfer should journey between your mind and muscle tissue. Relaying this info takes time. These physiological limits limit what sort of suggestions and decision-making processes can happen in the course of the execution of any specific motion.
Schmidt and Wrisberg describe a number of types of suggestions that happen at totally different timescales:
- Spinal twine reflexes. The quickest loop happens within the short-latency reflex (SLR, generally referred to as the M1 response). Right here an sudden change in muscular contraction sends a sign up your nerve to the spinal twine, the place a single synaptic connection sends again an acceptable motor nerve response. It takes solely 30-50 milliseconds and is each unconscious and rigid.
- Ready reflexes. Taking 50-80 milliseconds, the long-latency reflex, generally referred to as the M2 response, is slower than the SLR however extra amenable to deliberate preparation. Right here the directions to “maintain the burden regular” or “let go should you really feel extra stress” would modulate the response. However, like SLR, it’s nonetheless an unconscious reflex with restricted flexibility.
- Voluntary changes. After 120-180 milliseconds, info has time to journey to the mind and obtain deeper processing. Hick’s Legislation, which relates the delay in response time to the variety of alternatives, operates right here, suggesting that cognition is now concerned (even when the quickest actions might not have a lot aware deliberation).
For expertise that happen over an extended timeframe, like threading a needle, we will use a closed-loop system of suggestions, the place the total vary of sensations can be utilized to regulate our actions whereas performing the duty.
In distinction, for expertise that happen over quick intervals of time, suggestions is simply too sluggish. Thus, our brains must plan your entire motion prematurely, with restricted risk for adjustment if these actions turn into incorrect.
For example, a baseball pitch can journey as much as 90 miles per hour, that means your entire time between the ball being thrown and it reaching the plate is lower than 500 milliseconds. The batter wants 120-180 milliseconds for voluntary motion preparation and one other 140-160 milliseconds to swing the bat. Meaning the batter should determine if and how you can swing the bat earlier than the ball has traveled midway to the plate!
Planning Actions in Advance: Generalized Motor Applications
The timing constraints on open-loop actions indicate that a lot of our actions should be ready prematurely. One principle for the way we do that is that we assemble motor packages. These packages act like little scripts telling our muscle tissue when to maneuver with a view to produce the best actions.
If the motor program principle is appropriate, it additionally has main implications for studying motor expertise. Since motor packages are the constructing blocks of expert motion, studying motor expertise seemingly includes buying a big library of those packages (in addition to the perceptual and decision-making facility to make use of them in the best conditions).
What precisely is a motor program?
One risk is simple to rule out. If motor packages are the constructing blocks of talent, they don’t seem to be organized by way of express directions for how you can transfer every muscle.
Think about signing your identify. This fast, fluent motion is presumably saved in a motor program someplace in your mind. The idiosyncrasies of this motion are what make your signature distinctive. For those who signal your identify in a checkbook and on a chalkboard, the 2 signatures preserve the identical traits.
Nonetheless, if you consider it rigorously, the muscle tissue concerned in making the actions are fully totally different—writing on a checkbook primarily includes transferring your fingers and wrist, whereas writing on a chalkboard primarily includes transferring your shoulder and elbow whereas your wrist and hand keep largely mounted.
Thus, no matter a motor program is, it must be extra summary than easy instructions to contract specific muscle tissue. It has to signify the thought or desired end result of a motion, whereas presumably lower-level elements of the central nervous system are charged with implementing it.
Schmidt’s contribution to this principle was the notion of a generalized motor program. He argues that motor packages are saved within the mind as summary buildings. Among the facets of the packages are mounted, however there are additionally parameters that we will modify on the fly to change the motion for the present state of affairs.
What facets of motor packages are mounted, and that are free parameters?
We’ve already defined that the precise muscle tissue concerned in producing a selected motion are most likely a free parameter (explaining the an identical signatures on chalkboards and checkbooks). Amplitude might be one other (write the identical signature large or small). Power, pace and trajectory are additionally elements that seem like free parameters, quite than being mounted.
One factor that probably does look like mounted is the rhythm and relative timing of a motion. In a single experiment, members realized a process by which they practiced urgent keys in a selected order underneath particular timing necessities. After a whole lot of trials, members have been then requested to supply the sequence of keystrokes as quick as potential. Whereas they shortened the general time to carry out the skilled routine, the rhythm of key presses remained the identical (regardless that they weren’t requested to breed the rhythm realized in coaching).
This means that adjustments to the relative timing of a posh motor program might require studying a brand new motor program, quite than merely making use of a unique set of parameter values to an present one. A coach who desires an individual to make use of a unique rhythm of actions to supply a tennis serve might have a a lot larger job forward than the coach who simply desires the participant to hit more durable or increased.
How Can We Study Motion Expertise Extra Effectively?
Given the conceptual mannequin Schmidt and Wrisberg current, and the idea of generalized motor packages, what can we are saying about studying motion expertise?
Variable apply beats repetitive coaching for versatile expertise.
One space of energetic analysis in each mental and motor expertise is the worth of assorted apply. In lots of research, variable apply leads to extra sturdy or generalizable studying than extra repetitive types of apply.
Two forms of variability deserve notice:
- Random apply (vs. blocked). Suppose that you must apply each a forehand and backhand tennis stroke. One technique can be to drill forehand photographs for some time after which swap to backhand photographs. One other can be to randomize which shot that you must take, mixing each forms of motion collectively. Analysis typically helps the concept the latter apply schedule shall be simpler for studying, even when it tends to end in worse instant efficiency.
- Diversified apply (vs. constant). In distinction to easily mixing collectively several types of duties in coaching, different apply includes altering up the goals of the skilled motion. Think about hitting a golf ball on the driving vary vs. taking part in a spherical of golf. On the driving vary, you repeatedly hit the ball off the identical tee, in comparison with hitting it from a number of places to totally different distances alongside the course as you play. Diversified apply tends to be simpler for producing extra versatile motor packages that may adapt to new conditions.
Random apply gives for extra strong studying of the underlying program, and different apply helps to generalize the motor program so it may be efficiently parameterized in all kinds of settings. The primary exception to this precept happens within the very early phases of studying, when the motion will not be but absolutely understood. Cognitive load could also be increased right here, so including further problems might make it more durable to understand the underlying motion.
Determine the correct amount (and sort) of suggestions.
The significance of suggestions is obvious within the conceptual mannequin Schmidt and Wrisberg focus on. For closed-loop expertise and complicated performances, we modify our actions primarily based on a number of loops of suggestions from the setting.
Given the significance of suggestions, it may appear that extra is all the time higher. However this isn’t the case. Schmidt and Wrisberg notice a number of constraints on suggestions, noting the place it could actually do extra hurt than good:
- Concurrent and instantaneous suggestions might distort efficiency. Suggestions offered in the course of the execution of a talent might end in a unique talent being realized than the one supposed. Because the authors write, “concurrent visible suggestions is often disastrous for studying,” including, “fully totally different neural pathways are used.” Equally, suggestions that’s given immediately after a efficiency (quite than after a number of seconds of delay) might inhibit performers from studying and processing intrinsic indicators from the setting straight.
- Extra suggestions is best, however not on each try. Larger absolute ranges of suggestions have a tendency to enhance efficiency, however increased ratios of suggestions to no-feedback makes an attempt don’t all the time accomplish that. Higher outcomes usually happen with exterior suggestions on solely a portion of trials.
- Easier duties profit from sparser suggestions. Abstract suggestions, the place suggestions is aggregated over a number of trials, usually outperforms suggestions given after every try. The diploma of aggregation, nonetheless, depends upon complexity—novel or extremely complicated expertise profit from much less aggregation, whereas easier expertise profit from extra.
- Just one piece of recommendation at a time. Corrective options must be saved so simple as potential, in order to not overwhelm a performer’s restricted working reminiscence bandwidth.
Focus your consideration exterior your physique.
For the reason that motor packages that type the premise for expert actions embody an summary “thought” of the motion, not particular instructions to particular person muscle tissue, paying an excessive amount of consideration to your actions could be counterproductive.
A variety of research discover that an exterior focus of consideration, i.e., taking note of the purpose of the motion quite than the motion itself, is extra profitable for studying many various motor expertise. For example, in a single examine, golfers advised to give attention to the motion and weight of their membership did higher studying to make a chip shot than golfers advised to give attention to their grip and arm actions.
Regardless of this typically invaluable recommendation, there’s nonetheless some uncertainty within the analysis literature about precisely which parts of the exterior focus deserve extra consideration. In a single examine, golfers realized to swing higher when specializing in the motion of their membership, quite than the ensuing motion of the ball. But, in a unique examine tennis gamers realized higher once they have been advised to give attention to the trajectory of their shot, quite than the motion of the approaching ball.
Additional Ideas and Studying
Total, I discovered Schmidt and Wrisberg’s textbook to be an excellent useful resource protecting many fundamental ideas of motor expertise, particularly in emphasizing some facets that differ from the extra educational and mental expertise that I sometimes write about.

